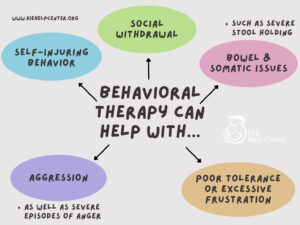
 Children with HIE, cerebral palsy, and other disabilities may sometimes develop behaviors such as:
Children with HIE, cerebral palsy, and other disabilities may sometimes develop behaviors such as:
- Aggression
- Severe episodes of anger
- Poor tolerance or excessive frustration
- Self-injuring behavior
- Social withdrawal
- Bowel and somatic issues (such as severe stool holding)
Behavioral therapies seek to reduce the incidence of maladaptive behaviors, instead encouraging positive behaviors in their place. This therapy focuses on providing incentives and rewards for positive behaviors in an effort to promote a child’s adaptive abilities and communication skills. The underpinnings of this therapy involve positive reinforcement rather than punishment. Another name for behavioral therapy is ‘behavior management’ or ‘behavior modification therapy.’
Sometimes, behavior therapy is combined with cognitive therapy to develop a therapeutic regimen called ‘cognitive-behavioral therapy.’ This therapy focuses not only on behavior, but also a child’s conscious thought processes and emotion. This therapy tries to ‘re-train’ the child’s negative thoughts and behaviors into an overall more positive outlook.
Behavioral Therapy Practitioners
There are several different practitioners that can help children and families with behavioral difficulties if needed. Child psychologists and social workers are trained in general behavioral techniques, though parents can receive training through seminars sponsored through their local school district, disability organization branch, or parenting course provider. Specialized behavioral therapists may be a more expensive option, but these practitioners have more specialized or specific training in many cases, and can often assist one-on-one in developing a treatment plan for use at home. School behavioral therapists can also work with teachers in developing plans for driving adaptive behaviors in the educational setting.
Types of Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy can sometimes be combined with social skills therapy to help individuals struggling with interacting with their peers and other people in their environment. Social skills therapy helps these children develop techniques for interacting positively with others. Individual hospitals may sometimes provide these services; the best way to determine service availability is to call local service providers and ask about their program offerings.
It is important to note that there are many different types of behavioral therapies, and not all of them are equally well-researched. Some therapies are well-researched, while many others are billed as ‘evidence-based’ but don’t meet the standards of rigorous scientific study to conclusively prove their effectiveness. Interventions typically considered effective include Discrete Trial Training (DTT), Functional Communication Training (FCT), and Pivotal Response Training (PRT), among others. Early Intervention is considered exceptionally important in ensuring therapy is effective. Social Skills Training and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are considered effective, as is Behavioral Support planning. Therapies considered promising include Developmental Relationship-Based Treatment (known as Floortime, DIR, or RDI), Play Therapy, and certain Supportive Therapies.
Sensory Integration Therapy (SI)
Sensory Integration Therapy (SI) is a very popular therapy but also controversial due to the lack of evidence surrounding its efficacy. Similarly, Auditory Integration Training (AIT), nutritional supplemental, gluten- and casein-free diets, and facilitated communication (FC) have not been scientifically proven to work.
Learn More About Behavioral Therapy
Some therapies for children with autism are sometimes also prescribed to children with developmental delays and/or disabilities. A list of evidence-based interventions can be found at the National Professional Development Center on Autism Spectrum Disorder, the Illinois State Board of Education website, and the following comprehensive Missouri Autism Guidelines Initiative’s Guide to Evidence-Based Interventions. Other behavioral therapy resources include:
- My Child Without Limits: Behavior Therapy [Overview]
- Options for Treating Social Skill Limitations
- [Research] Treating Individuals With Intellectual Disabilities and Challenging Behaviors With Adapted Dialectical Behavior Therapy
- [Research] Dialectical Behaviour Therapy [DBT] with People with Intellectual Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Narrative Analysis