No two cases of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) are exactly alike. Brain injuries stemming from HIE can lead to a variety of associated health conditions and disabilities. The way HIE affects an individual child depends on what parts of the brain were injured & the extent of the damage.
 Children with severe HIE may develop motor disorders such as cerebral palsy, intellectual disabilities, speech-language problems, or hearing and vision impairments. Many kids end up having a combination of these issues, as well as other serious health concerns.
Children with severe HIE may develop motor disorders such as cerebral palsy, intellectual disabilities, speech-language problems, or hearing and vision impairments. Many kids end up having a combination of these issues, as well as other serious health concerns.
Doctors may be able to provide a general initial prognosis, but it can be difficult to know exactly what long-term disabilities a child will develop at that time. Although the brain injury itself does not worsen, it may have secondary effects that evolve as the child grows and matures. Additionally, certain issues may not become apparent until the child starts to show signs of developmental delays such as not walking, talking, or learning to read around the same time as their peers.
The following conditions, injuries and/or disabilities may occur as a result of birth asphyxia and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Learn more about these possible long-term outcomes:
- Cerebral palsy
- I/DD (intellectual/developmental disabilities)
- Learning disabilities
- Fetal stroke
- Intracranial hemorrhages (brain bleeds)
- Epilepsy, seizures, and seizure disorders
- Speech delays and language disorders
- Behavioral and emotional disorders
- Hearing and vision limitations
- Nutritional concerns
- Oral health problems
- Neurologic and mental health concerns
- Skin health concerns
- Orthopedic conditions
- Pain
- Respiratory conditions
- Sensory processing issues
Some effects of these conditions can be mitigated with optimal treatment, therapy, supportive equipment, and assistive devices. To learn more about existing and potential treatments for HIE, please click here.
The importance of therapeutic hypothermia
If neonatal HIE is recognized very shortly after the birth injury (oxygen deprivation) occurs, the permanent effects may be minimized with a treatment known as therapeutic hypothermia.
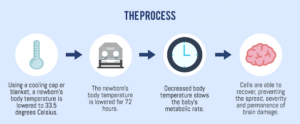
Therapeutic hypothermia gives damaged cells time to recover from asphyxia, which lessens the spread of permanent brain injury. Failure to perform therapeutic hypothermia and other important treatments in the immediate aftermath of an hypoxic-ischemic injury is medical malpractice.
This underscores the importance of recognizing HIE as soon as possible. Medical professionals should evaluate babies for HIE if they:
- Experienced delivery complications which put them at high-risk of brain injury
- Showed signs of fetal distress (such as an abnormal heart rate) during birth or if
- Are showing early signs and symptoms of HIE
Once HIE is suspected, doctors should perform diagnostic tests and evaluations, including neuroimaging methods such as:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Umbilical cord blood gas tests and
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
About the HIE Help Center
The HIE Help Center is run by ABC Law Centers, a medical malpractice firm exclusively handling cases involving HIE and other birth injuries since the firm’s inception in 1997. If you suspect your child’s HIE may have been caused by medical negligence, contact us to learn more about pursuing a case. We provide free legal consultations, during which we will inform you of your legal options and answer any questions you have. You pay nothing throughout the entire legal process unless we obtain a favorable settlement.

